For people of color, dark spots and small areas of hyperpigmentation are a constant struggle. This is especially true in darker skinned people who also suffer from acne and have sensitive skin. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) is one of the most common skin complaints to dermatologists. One of the main initial solutions for this problem is dark spot correctors.
Common ingredients that reduce dark spots or brighten skin include: vitamin C; hydroquinone; kojic acid; retinol (or other retinoids); niacinamide; exfoliating acids and peels such as glycolic acid and salicylic acid; licorice root extract; tranexamic acid; azelaic acid; arbutin; and emblica. Daily use of sunscreen is also a requisite if you want to achieve an even toned skin.
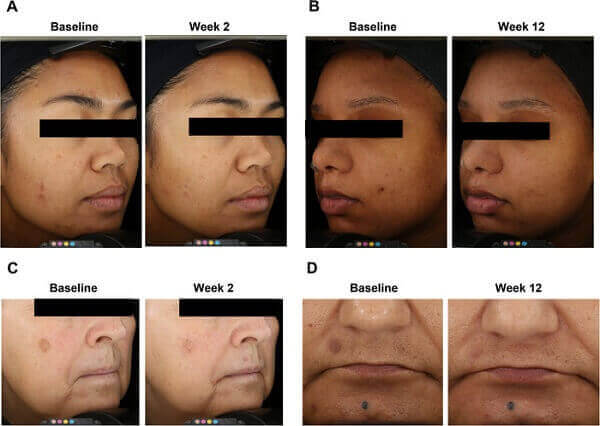
A recent 2023 study showed that a novel pigment-correcting dark spot treatment gel significantly improved the appearance of PIH and solar lentigines after 12 weeks of application. Below is the before and after photo.
The Best Dark Spot Correctors in 2024
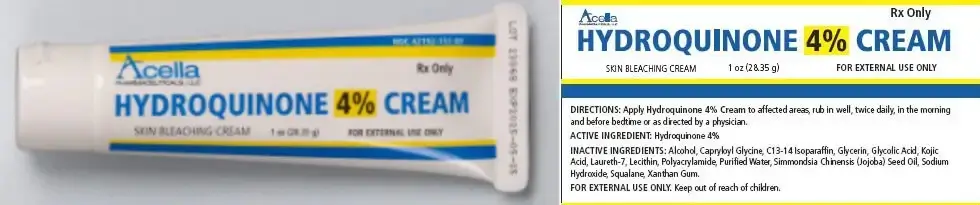
There are numerous dark spot correctors on the market. Most can be used safely by people with all skin types. However, some of them contain ingredients that should be used sparingly by people with darker skin types. Lightening creams with hydroquinone can especially cause serious side effects with long-term use on dark skin.

TruSkin’s Vitamin C Serum is a good first step to begin lightening your facial dark spots. While it doesn’t contain any potent ingredients, this means that there are less chances of undesirable side effects. With over 142,000 Amazon reviews at the time of writing this post, this product is a blockbuster. The average rating of 4.3 out of 5 stars is also respectable.
Besides Vitamin C, this TruSkin Serum also contains Hyaluronic Acid and Vitamin E. It contains a better form of Vitamin C (Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate) that is highly stable and maintains potency for longer. It also causes less skin stinging than other commonly used forms of Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid).

What would any bestselling list of skincare products be without the mention of French cosmetics behemoth L’Oréal? The company’s Bright Reveal dermatologist tested dark spot serum contains a very strong 12% Niacinamide as well as Amino Sulfonic Acid and Ferulic Acid.
It will visibly reduce the appearance of dark spots, age spots, sunspots and post-acne scar marks. The Ferulic Acid and Amino Sulfonic Acid gently exfoliate skin surface cells and moisturize and brighten skin.
Cysteamine is a very unique novel ingredient. The Cyspera pigment correction cream contains Cysteamine Isobionic-Amide Complex™. It inhibits both tyrosinase and peroxidase. It also acts as a dopaquinone scavenger. The Cyspera Intensive System costs $285 on the manufacturer’s website and consists of:
Cyspera Intensive™ (30 ml / 1 fl oz).
Cyspera Neutralize™ (50 ml / 1.75 fl oz).
Cyspera Boost™ (30 ml / 1 fl oz).
Musely makes a range of products to diminish your dark spots and hyperpigmentation. Among the ingredients in their prescription dark spot reducing cream include hydroquinone, niacinamide, azelaic acid, tretinoin, hydrocortisone, tranexamic acid and vitamin C. Getting prescription from Musely is easy and all done online via a 3-minute doctor consultation. Your custom medication is then compounded and mailed to you. If you have dark skin, make sure that you go easy on the hydroquinone strength and frequency of application. Overuse can cause long-term skin damage.
Discoloration Serum from Good Molecules
Good Molecules Discoloration Correcting Serum currently has 3,500 reviews on Amazon, with an average rating of 4.3 out of 5 stars. Currently prices at $12 for 1 Fl Oz. The key ingredients in this product are 3% tranexamic acid (cetyl tranexamate mesylate) and 4% niacinamide. The tranexamic acid targets skin discoloration and helps promote a clear skin tone. Make sure to read my post on tranexamic acid for skin lightening. The niacinamide helps improve the appearance of uneven skin tone, dullness and enlarged pores.
Clinique Dark Spot Corrector Interrupter

This is a very expensive product when not on sale, retailing at $88 for a 1.7 Fl Oz serum pump. The currently discounted price is $26. It has an average rating of 4.3 out of 5 stars based on 2,030 reviews. All Clinique products are free from parabens, phthalates and fragrance.
The key ingredients in Clinique’s unisex dark spot corrector and interrupter are salicylic acid, vitamin C and proprietary CL302 equalizer technology. Its use results in diminished acne scars and dark spots.
Topicals Faded Brightening and Clearing Serum

Topicals Faded Brightening and Clearing Serum contains Kojic Acid, Niacinamide and Tranexamic Acid. It is dermatologist tested, vegan and cruelty-free and also contains Allantoin, Azelaic Acid and Licorice Root Extract.
The 1.7 Fl Oz tube of Topical Faded currently costs $38, which is moderately expensive. The average rating across 1,830 reviewers is 4.1 out of 5 stars. Topicals Rx is listed as a small black-owned business and its products are always suitable for black skin.
Neutrogena Dark Spot Corrector

Well known brand Neutrogena makes a dark spot corrector with Retinol and Vitamin C as the key ingredients. It currently has almost 10,000 reviews with an average rating of 4.2 out of 5 stars. It targets stubborn dark spots to even out skin tone.
This daily facial serum is formulated with fast acting pure retinol, a dermatologist-approved and proven form of vitamin A. It is suitable for daily use in all skin types (including South Asian and Black), and is free of mineral oil and dyes.
AXIS-Y Dark Spot Correcting Glow Serum
An interesting product from South Korea that contains 5% niacinamide, vegan plant-derived squalane, papaya extract, allantoin, rice bran, sea buckthorn, calendula and more. Note that squalane is the hydrogenated derivative of squalene. Helps reduce the appearance of dark spots and hyperpigmentation and brightens skin. AXIS-Y currently has currently has 2,800 reviews on Amazon, with an average rating of 4.3 out of 5 stars.

The CITYGOO dark spot remover cream tranexamic acid, niacinamide, squalene, panthenol, citric acid, vitamin E and hydrolyzed rice protein. It claims to reduce dark spots, pregnancy spots, sun spots, hyperpigmentation, scars, discoloration and melasma.
The Lightning Wand from Hero Cosmetics is a brightening serum for fading dark spots. It contains powerful skin care ingredients and yet no hydroquinone, phthalates, artificial color, no fragrance. It is also not tested on animals. Glycolic acid in this Lightning Wand product exfoliates dead skin. The skin is also brightened with vitamin C, niacinamide and tranexamic acid.